

While diffraction occurs whenever propagating waves encounter such changes, its effects are generally most pronounced for waves whose wavelength is roughly comparable to the dimensions of the diffracting object or slit. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1660. Since physical objects have wave-like properties (significantly at the atomic level, invisibly at macro level), diffraction also occurs with matter and can be studied according to the principles of quantum mechanics. Diffraction occurs with all waves, including sound waves, water waves, and electromagnetic waves such as visible light, X-rays and radio waves. Diffraction has an impact on the acoustic space. Similar effects occur when a light wave travels through a medium with a varying refractive index, or when a sound wave travels through a medium with varying acoustic impedance. These characteristic behaviors are exhibited when a wave encounters an obstacle or a slit that is comparable in size to its wavelength. In classical physics, the diffraction phenomenon is described as the interference of waves according to the Huygens–Fresnel principle that treats each point in the wave-front as a collection of individual spherical wavelets.
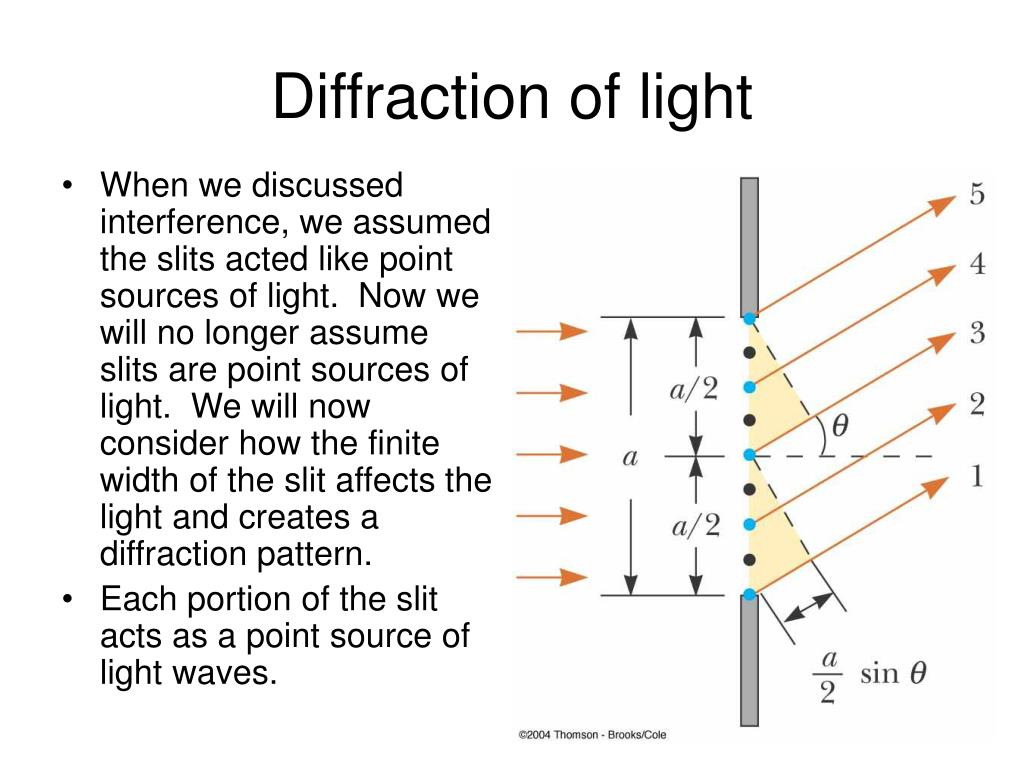
It is defined as the bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle. Diffraction pattern of red laser beam made on a plate after passing through a small circular aperture in another plateĭiffraction refers to various phenomena that occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or a slit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
